Neurosciences Of Antioxidants

To immerse ourselves in the neurosciences of antioxidants is to go to the depths of the organism and see how it interacts with these molecules. Above all, to know how they favor us and with what variables they are related.
Thus, when speaking of neurosciences, we refer to a multidisciplinary field that is dedicated to the study of the nervous system. He does it from biology, psychology, medicine, engineering and education. Let’s dive deeper into the nervous system’s relationship with antioxidants!
Neurosciences of antioxidants: neurodegeneration
To understand the neurosciences of antioxidants, we must understand oxidative stress. It consists of a complex situation in which an imbalance occurs between the availability of antioxidants and the generation of reactive oxygen species.
All this accompanied by an ineffective selectivity of the blood-brain barrier that reduces the diffusion of essential antioxidants. For example, like vitamin E.
Antioxidants and diseases related to the nervous system
Oxidative stress has been studied in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease. In addition, it has been seen that oxidative damage could be related to the etiology of the disease, that is, to the origin.
It happens that the nervous system consumes oxygen in large quantities to be able to carry out its functions. This increases the production of free radicals. However, the escape of reactive oxygen species from antioxidant mechanisms and their progressive accumulation causes structural damage to some proteins.
According to Díaz-Hung and González Fraguela, in the article they published for the Spanish Neurology Society, these molecular alterations are excessive in neuronal populations of pathological processes such as Alzheimer’s disease and affect pyramidal neurons, the substantia nigra and the cortex. parietal, among others; areas that are affected in these diseases.
Now, although there is evidence that highlights the importance of antioxidant mechanisms in relation to these pathologies. The use of antioxidants as protection has given negative result, especially with vitamin C and E.
Although, authors such as González-González, Pérez-Cortéz, Flores-Aldana and Macías-Morales, in their published article Medwave , suggest that lipolic acid has been well tolerated in the clinical treatment of multiple sclerosis. They reached this conclusion after a literature review in relation to multiple sclerosis and diet.
Furthermore, oxidative stress has been linked to neuronal hyperarousal, changes in membrane fluidity, and neuronal loss in the cerebellum; issue that could be related to autism spectrum disorders and epilepsy.
Integral nutrition
As we have been saying, antioxidants are compounds capable of inhibiting the oxidation of lipids. This activity can play an important role in neutralizing free radicals, thus protecting cells.
Therefore, its consumption is essential for the preservation of the body’s functions. In fact, they help fight the deterioration caused by cellular aging. However, we cannot see this consumption as the solution to all ills. It helps, but it is important to maintain a balanced nutrition.
In addition, in case of having any of the aforementioned diseases, we will do well to give it the attention it requires. In all cases, consulting with a professional is the smartest measure.
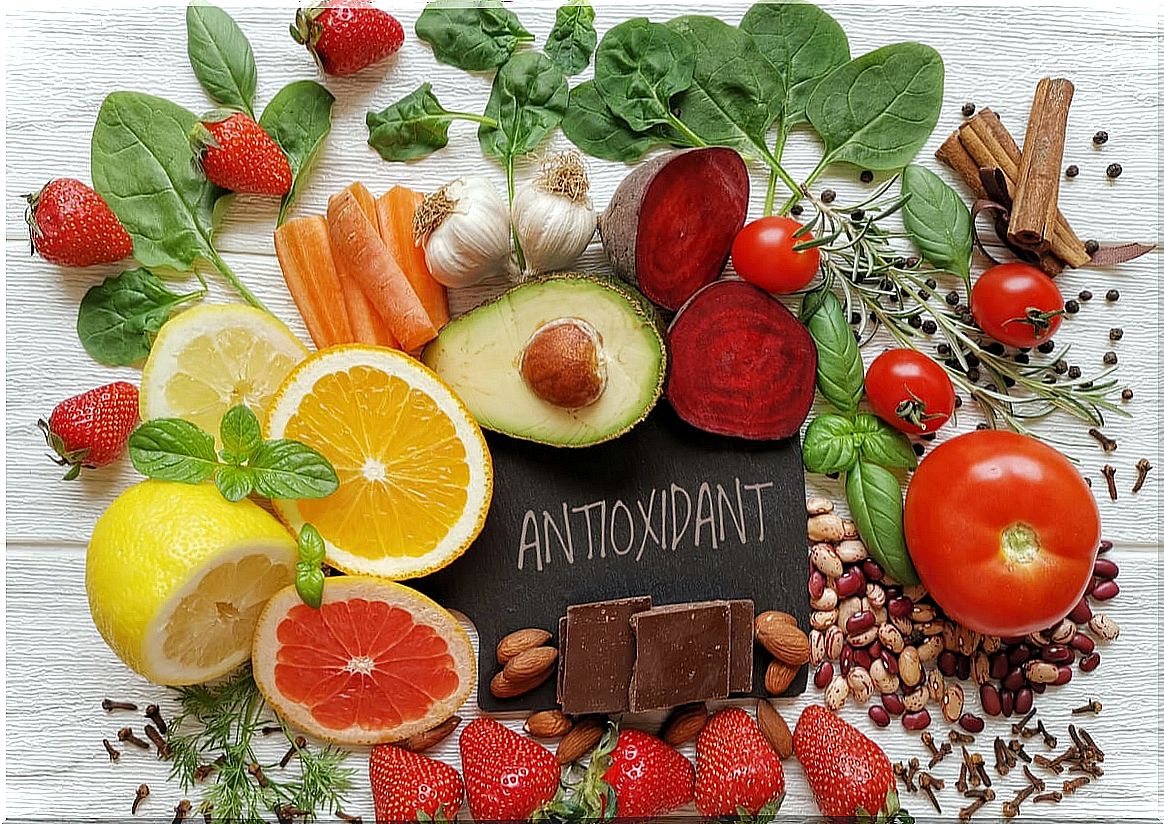
Now, what foods are rich in antioxidants? Citrus fruits, like cauliflower, spinach, soybeans, and bell peppers. That is, we find them in carotenes, lipocenes, selinium and vitamins A, C and E. As we see, if we have a balanced diet, they are usually present almost by default.

Neurosciences of antioxidants and cognitive performance
Cognition, that is, can benefit from the consumption of antioxidants. How? The Mediterranean diet favors cognitive functions. Its high content of polyphenols, molecules that counteract the cognitive decline associated with aging due to its antioxidant function, favors the elimination of free radicals caused by oxidation.
In this sense, the use of nutrients in the appropriate proportions would contribute to improving health. Not only physically but mentally. However, we still need more studies for the evaluation and comparison of different practical results to fully understand how it works. Above all, to find a way to modulate or delay neurodegenerative diseases through the mechanisms and action of antioxidants.
In short, antioxidants strengthen healthy nutrition, helping us to add steps to improve our quality of life. They seem to play an essential role in the prevention of cellular aging and to be related to neurodegenerative diseases. However, we do not have a clear theory, beyond its use as a preventive factor, accompanied by other factors.









